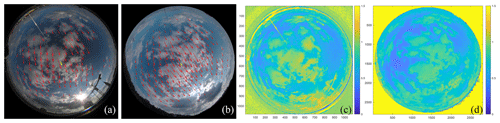
Solar PV nowcasting based on skycamera observations
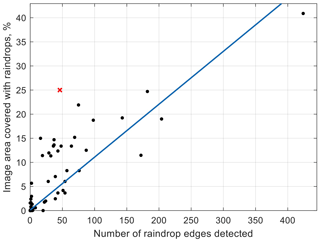
In recent years the installation of PV systems has increased dramatically in many countries. Annual global installed power has already reached more than 400 GW in 2017. A major challenge for operators is that PV system output is highly fluctuating due to cloud movements and other atmospheric influences. Forecasting of solar irradiation and PV power on different time scales will, therefore, become more and more important for different users. As part of the Austrian PV-go-Smart project, several skycameras have been installed in the region of Upper Austria. In this paper we show differences and advantages of two skycams and their image qualities. Algorithms for the detection of clouds, cloud movement, and GHI forecasting have been developed and validated with ground observation at the Wels site. This work focusses on image quality issues related to short-term irradiance forecasting using all-sky cameras, in particular the influence on raindrops on forecast performance.